Eye injuries are a common but major health issue affecting people of all ages. From little cuts to major tragedies, eye injuries can cause discomfort, visual problems, or even blindness if not quickly addressed. Maintaining eye health and avoiding long-term damage requires awareness of the origins, symptoms, and available treatments.
This article discusses several kinds of eye injuries, their causes, symptoms to be alert for, treatment approaches, and preventative advice. Knowing how to react can make all the difference, whether a sports-related injury or an office accident.
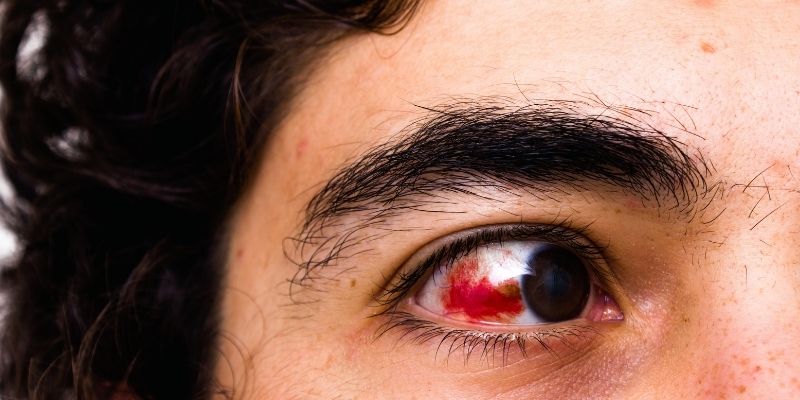
Common Causes of Eye Injuries
Eye injuries can happen in many different surroundings and situations. The eyes are vulnerable, whether at home, at work, or engaged in leisure activities. Some such reasons are:
- Blunt Force Trauma: Objects striking the eye can cause serious injury in accidents. Sports, auto mishaps, or violent confrontations could all lead to this.
- Foreign Objects: Easy entry of dust, dirt, sand, or other particles into the eye causes irritation, corneal abrasions, or sometimes infections.
- Chemical Exposure: Unintentional droplets from industrial chemicals, cleaning agents, or other toxic compounds can seriously damage the eye.
- Radiation: Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun, welding torches, or tanning beds can damage the eyes, possibly resulting in burns on the cornea (photokeratitis) or helping to produce cataracts.
- Penetrating Injuries: Sharp items like knives, glass fragments, or metal can cut internal structures severely by getting into the eye.
- Burns: Severe eye damage can also come from thermal burns from hot liquids, fires, or explosions.
The probability of eye damage can be much lowered by awareness of these hazards and implementing preventative actions.
Symptoms of Eye Injuries:
Timely treatment depends on an awareness of the indicators of eye damage. The degree and nature of the damage will affect the symptoms. Among the typical indicators to be on alert are:
- Pain Or Discomfort: Mild irritation to the extreme. Acute pain is the spectrum of eye discomfort.
- Blurred Or Reduced Vision: Suddenly changing vision clarity could point to an eye injury.
- Redness: Red or bloodshot eyes would indicate ocular irritation, infection, or damage to the blood vessels.
- Swelling: Trauma frequently shows up as swelling around the eye, eyelid, or eye socket.
- Sensitivity To Light: Should your eyes grow more light-sensitive following an injury, this could indicate damage.
- Discharge: Pus or other ocular discharge could point to an infection brought on by an accident.
- Bleeding: Internal or external bleeding in or around the eye is a frightening indication that calls for quick attention.
If any of these symptoms linger following an injury, visiting a doctor is crucial. Untreated eye injuries can cause permanent damage or vision loss.
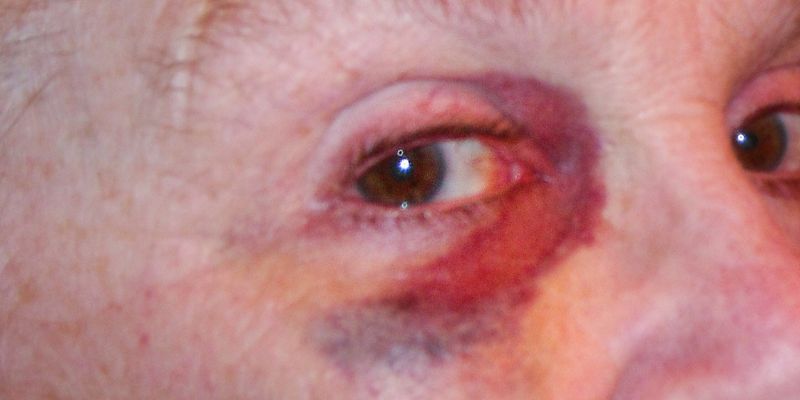
Types of Eye Injuries
There are various kinds of eye injuries, each with different degrees of seriousness and treatment needs. Among the most often occurring ones are:
- Corneal Abrasions: Surface of the cornea scratches resulting from dust, debris, or microscopic particles. Pain, redness, and a sensation of something caught in the eye comprise symptoms.
- Black Eye: Blunt force trauma produced a bruise around the eye. Usually healing in a few weeks it may cause oedema and discoloration.
- Chemical Burns: These burns result from dangerous chemicals that need medical attention and instantaneous cleaning with water.
- Penetrating Eye Injuries: Sharp objects can cut the eye and cause extreme internal damage and vision loss. These wounds need emergency care.
- Foreign Objects: Little particles like metal shavings or dust can irritate or damage the eye. While most foreign objects are readily removable, some could call for medical care.
- Detached Retina: More extreme damage whereby the retina separates from the eye. Signs include visual loss, floaters, and flashes of light.
Knowing these kinds of injuries would enable people to appreciate the gravity of their illness and get suitable treatment.
Treatments for Eye Injuries
The type and degree of eye damage will affect the therapy course. While more serious cases require rapid medical attention, minor injuries could need basic first aid. Typical treatments include:
- Flushing the Eye: This is the first line of therapy for chemical damage or when foreign items are involved in ocular cleansing with water. It aids in the elimination of toxic elements or particles.
- Eye Drops: prescription eye drops could help heal the damage and relieve mild annoyances.
- Pain Relief: Overthecounter painkillers can ease the suffering of minor injuries.
- Antibiotics are recommended if an infection is present or anticipated, typically in ointments or eye drops.
- Surgery: Severe eye injuries, including retinal detachment or piercing damage, could require surgery to restore vision or prevent loss.
- Eye Patching: Sometimes, doctors advise covering the damaged eye with a patch to encourage healing and prevent further irritation.
The prevention of problems and guaranteeing the greatest possible recovery depend on early treatment.
Prevention of Eye Injuries
Usually, preventing eye injuries at work is simpler than treating one. Simple actions can greatly lower daily life's risk of harm, particularly in settings where the eyes are more exposed. Important preventive plans consist of the following:
- Wear Protective Eyewear: In settings where flying debris, chemical exposure, or radiation (e.g., building sites, labs, or during sports) are present, safety glasses, goggles, or face shields should be worn.
- Take Care During Sports: Many activities, including racquetball, baseball, or basketball, can cause eye damage. Wearing suitable protective gear can help lower these hazards.
- Handle Chemicals Safely: When handling chemicals, always wear goggles or face protection. Check that containers are kept correctly and tightly sealed.
- Follow Safety Protocols: Follow safety protocols when operating machinery or working in dangerous surroundings at the office. Take breaks and rest your eyes when working lengthy stretches on displays.
- Be Mindful Of Children. Children are prone to eye damage from toys, pointed objects, or rough play. Ensure age-appropriate toys and supervise to help avoid mishaps.
Using these easy preventative strategies will greatly help preserve your vision.
First Aid for Eye Injuries
Knowing what to do immediately following an eye injury helps stop more damage and speedier healing. That is a guide on first aid for several forms of eye injuries:
- For foreign objects, Avoid rubbing your eyes. Try flushing them using either a saline solution or pure water. If the object is embedded, get medical attention right away.
- For Chemical Exposure, Water should constantly flush the eye for at least fifteen minutes. If applicable, remove your contact lenses and get immediate help.
- For Blunt Trauma: Use a cool compress to help with swelling; steer clear of pressing right on the eye. Should symptoms get worse, seek medical attention.
- For Cuts Or Punctures: Avoid clearing anything caught in your sight. Rather, cover the eye loosely with a fresh cloth and get immediate medical attention.
In eye injuries, a little first aid knowledge can save lives.
Conclusion:
Eye injuries can include mild irritations to major damages endangering eyesight. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and accessible therapies helps you respond quickly to eye damage and lower your long-term risk of consequences. Minimizing injury risk depends greatly on preventative actions like safety procedures and wearing protective eyewear. Years of healthy eyesight will depend on regular eye exams and quick care.













