Advertisement
Pulp necrosis indicates a condition of the tooth in which the living tissue, i.e., the pulp, undergoes degenerative changes and necrosis. As a result, the tooth becomes non-vital, and the sensations are lost. It may be due to a blunt injury that does not exhibit any symptoms at first, but slowly, the inflammatory changes occur, and the tooth becomes non-vital. Dental caries can also spread and cause necrosis of the pulp.
There are several causes of pulp necrosis, but the most common causes are mentioned below.
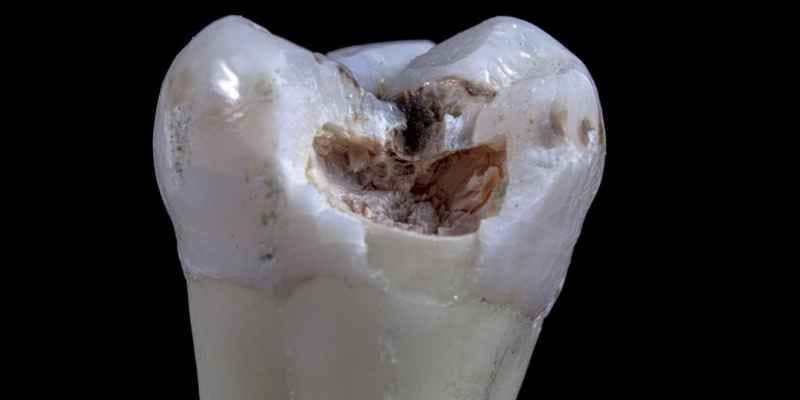
The most common symptoms of pulp necrosis are:
Several complications can arise from the condition of pulp necrosis. These conditions include:
Spread of infection:
If pulp necrosis may go unnoticed, it can lead to the spread of infection. The pathogens may slowly spread in spaces and cause disease. From the tooth, the infection can spread to the throat, neck, and even chest if not treated promptly.
Dental abscess formation:
As the infection spreads and the bodys immune response activates, there is a resultant death of white blood cells, resulting in pus formation. The formation of an abscess is indicative of an underlying pathology, i.e., in this case, the pulp necrosis that needs to be addressed immediately.
Necrosis of the jaw and bone:
Commonly, severe pulp necrosis leads to the necrosis of jaws. This happens as the infection and pathogens responsible for causing the pulp necrosis slowly travel through the surrounding bone, invading the areas of healthy bone tissue and replacing it with dead tissue. As a result, the necrosis of jaws can occur.
Sinus tract formation:
It can be seen in case of severe infection. If the infection remains entrapped within the specific tooth, it may appear on the face as a sinus tract, i.e., a drainage pathway from a deep focus to the surface opening.
Severe inflammatory changes:
An infection always accompanies inflammatory changes. In the case of pulp necrosis, the building pressure and inflammation to remove the debris from the tooth may result in the swelling of the external soft tissues like the face and neck. It proves to be unesthetic to the patient as well as cause functional problems like speech and mastication.
Several diagnostic procedures can be used to diagnose pulp necrosis. Some of the essential diagnostic tools used are given below.
The first step to reach an accurate diagnosis is history. It is vital to ask the patient about the duration and character of pain, as most dental diseases can be distinguished from pulp necrosis if an accurate history of pain is taken. Furthermore, it is crucial to ask about any history of trauma or tooth injury to rule out internal resorption.
It is vital to examine the tooth and the area surrounding it to check for any dental abscess, tooth discoloration, or even a sinus tract formation. Sometimes, the necrosis of bone may also appear in the oral cavity.
If there is pain while palpating the mucosa and structures surrounding the tooth, it indicates an underlying infection, like pulp necrosis. So, it is crucial to palpate the surrounding structures of the tooth to form an accurate diagnosis.
An icy and very hot object is allowed to come in contact with the tooth. In case of a response from the patient, the pulp tissue is alive and, its nerves are intact to carry sensations. However, in case of no response from the tooth, a pulp necrosis is indicated.
In this test, a particular device is used to provide varying amounts of electric current to the tooth. If the pulpal tissue is alive, there will be a response from the tooth. In the case of pulp necrosis, no pulp tissue is alive, and as a result, this test is negative, and no reaction is elicited.
Percussion test is done by tapping the dental mirror on the tooth. In the case of pulp necrosis, the inflammation and necrotic tissue exerts pressure and pain as it remains within a closed chamber. The result is a positive percussion test, which indicates an underlying inflammatory response.
A periapical radiograph indicates a radiolucent area, which is indicates pulp necrosis. Any other anomaly can also be detected easily on a radiograph to reach a confirmative diagnosis.
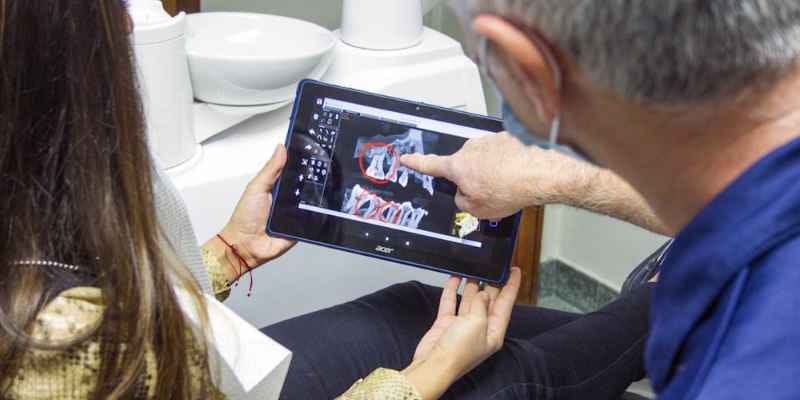

There are several treatment options that can be opted for a tooth with pulp necrosis. Some of these options are:
Medications like antibiotics and painkillers can treat the infection and pain accompanying pulp necrosis.
Root canal treatment can be done where there is a chance that removing the infection and necrotic tissue from the roots, followed by the treatment with gutta-percha, can restore the tooth. An RCT is usually the first treatment option to be considered for pulp necrosis.
Extraction is the option when no options are left to salvage the tooth, and its removal is the only way to eliminate the infection and its complications. An implant can be placed in the socket to compensate for the extracted tooth.
It is crucial to maintain excellent dental hygiene to avoid any subsequent diseases and complications. Regular visits to the dentist and scaling of the teeth have also been shown to improve oral health considerably.
Pulp necrosis is a condition that needs to be addressed promptly. If it is ignored or goes unnoticed, it can lead to severe complications.
Advertisement

By Verna Wesley/Oct 20, 2024

By Juliana Daniel/Mar 16, 2025

By Darnell Malan/Dec 23, 2024

By Susan Kelly/Mar 17, 2025

By Isabella Moss/Apr 01, 2025

By Susan Kelly/Dec 21, 2024

By Maurice Oliver/Oct 22, 2024

By Elva Flynn/Feb 19, 2025

By Aldrich Acheson/Dec 19, 2024

By Elena Davis/Oct 23, 2024

By Georgia Vincent/Dec 31, 2024

By Juliana Daniel/Oct 24, 2024